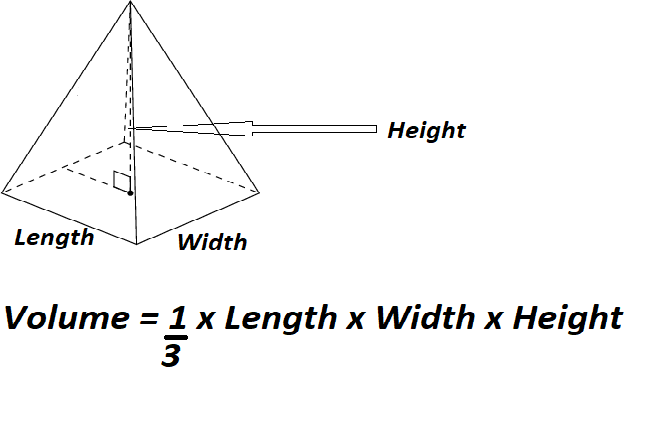
Volume is the quantification of the three-dimensional space a substance occupies. By convention, the volume of a container is typically its capacity, and how much fluid it is able to hold, rather than the amount of space that the actual container displaces. Volumes of many shapes can be calculated by using well-defined formulas. In some cases, more complicated shapes can be broken down into simpler aggregate shapes, and the sum of their volumes is used to determine total volume. The volumes of other even more complicated shapes can be calculated using integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape's boundary. Beyond this, shapes that cannot be described by known equations can be estimated using mathematical methods, such as the finite element method.
Alternatively, if the density of a substance is known, and is uniform, the volume can be calculated using its weight. This calculator computes volumes for some of the most common simple shapes. For example, the space that a substance or 3D shape occupies or contains. Volume is often quantified numerically using the SI derived unit, the cubic metre.
Volumes of some simple shapes, such as regular, straight-edged, and circular shapes can be easily calculated using arithmetic formulas. Volumes of complicated shapes can be calculated with integral calculus if a formula exists for the shape's boundary. One-dimensional figures and two-dimensional shapes are assigned zero volume in the three-dimensional space. The volume of water in ponds is often expressed in units called "acre-feet." An acre-foot represents one surface acre that is one foot deep.
To calculate the acre-feet of water in a pond, you'll need the surface area in acres as calculated above and an average depth of water in the pond. For a typical bowl-shaped pond the average depth can be estimated as 0.4 times the maximum depth. So, a pond with a maximum depth of 12 feet would have an average depth of about 4.8 feet. For regular three-dimensional objects, you can easily calculate the volume by taking measurements of its dimensions and applying the appropriate volume equation. If it's an irregular shape, you can try to do the very thing that caused Archimedes to shout the famous word Eureka! Probably you heard that story - Archimedes was asked to find out if the Hiero's crown is made from pure gold or just gold-plated - but without bending or destroying it.
The idea came to him when he was taking a bath - stepping into a bathtub, he noticed that the water level rose. From this observation, he deduced that volume of water displaced must be equal to the volume of the part of his body he had submerged. Knowing the irregular object volume and its weight, he could calculate the density and compare it with the density of pure gold. Legend says that Archimedes was so excited about this discovery that he popped out of his bathtub and ran naked through the streets of Syracuse.
Volume is an amount of space, in three dimensions, that a sample of matter occupies. The number and the phase of the molecules in the sample primarily determine the volume of a substance. Volume will be measured in many ways in this course, but the units are usually milliliters or cubic centimeters . Methods for determining or delivering precise volumes include volumetric pipets and pycnometers; less precise methods include burets, graduated cylinders, and graduated pipets. Cubic feet per second, sometimes written second-feet (sec. ft. or cusec) is most commonly used for measuring flow of irrigation water moving by gravity from streams and reservoirs.
Gallons per minute is most commonly used for measuring flow from pumps. ServiceTitan's pipe volume calculator makes a pipe calculation simple and easy. Measure the volume of pipes based on inner diameter and length. You can also use this calculator to tally how much the volume of water in pipes weighs.
A more accurate method for calculating average depth is to make many measurements and calculate an average. This is most often done by measuring the pond depth along two transects--one along the width and one along the length. Make sure to pick transects that represent the shallow and deep portions of the pond. Depths can be measured easily from a canoe or boat using a weight and a string marked in feet. The more depth measures that you make, the more accurate your final average will be. In the example shown on the next page, pond depths were taken at six locations across the pond length and five locations across the pond width.
The average pond depth can be calculated as the average of all of these measurements. The importance of getting an accurate estimation of your pond surface area cannot be overestimated. The majority of pond owners visually estimate their pond area, which usually results in an overestimate of the true pond surface area.
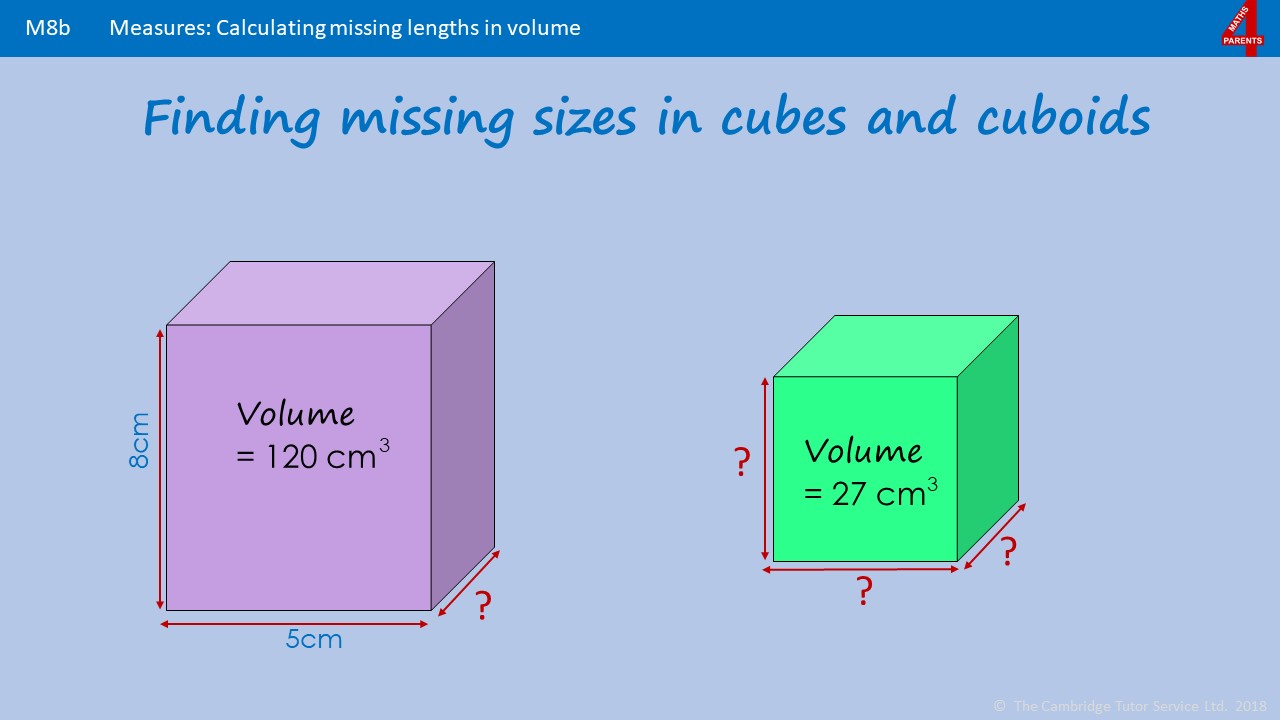
Pond area and water volume should be calculated based on some simple measurements. The effort necessary to estimate pond surface area is directly related to your pond's shape and uniformity. The simplest method--using basic equations for common shapes--can be applied if your pond closely resembles a circle, square, rectangle, or trapezoid in shape. The volume calculator will calculate the volume of some of the most common three-dimensional solids. Before we go into how to calculate volume, you must know the definition of volume.
Volume differs from the area, which is the amount of space taken up in a two-dimensional figure. So you might be confused as to how to find the volume of a rectangle versus how to find the volume of a box. The calculator will assist in calculating the volume of a sphere, cylinder, cube, cone, and rectangular solids. Volume is defined as a capacity occupied by a three-dimensional solid shape. In any shape, it is hard to visualize but can be compared between shapes. For example, the volume of a compass box is greater than the volume of an eraser placed inside it.
For calculating the area of any two-dimensional shape, we divide the portion into equal square units. Similarly, while calculating the volume of solid shapes we will divide it into equal cubical units. Let us learn how to calculate the volume of different solid shapes in our next section. Liters are a common measurement often used to measure beverages and other liquids, such as a 2 liter bottle of soda. Sometimes you will need to calculate the volume of an object in liters, given the object's dimensions.
In other instances, you will need to convert the volume of something that is already given in another unit, such as milliliters or gallons. In all of these instances, through simple multiplication or division, you can easily determine volume in liters. It's usually fairly easy to calculate the volume of a liquid in a container with a regular shape, such as a cylinder or cube. All you have to do is use the appropriate mathematical equation to calculate the capacity of the container, then measure the level of the liquid and make the necessary adjustment.
It's more challenging when the container doesn't have a regular shape, and that's most of them. The challenge disappears if you know the density of the liquid, though. All you have to do is weigh the container and the liquid, subtract the weight of the container, and use the density of the liquid to derive your answer. Unit of volume is cubic meter since volume is a quantity of the three-dimensional space occupied by a shape or surface. However, the most commonly used unit for volume is liter.
Apart from this, large and small volumes are measured in other units like milliliter , pints, gallons, and others. The following table shows a few units related to volume and its metric equivalents. The last group includes the volume of liquid left in the various vessels, lines, chiller, pump, etc.
Those values that depend on relationships are the boiling losses and any "top-off" water added to the kettle or fermenter. The remaining values, the volumes of strike water, water absorbed by the grain, any additional mash infusions and the sparge water, can be calculated from the recipe. Length times width gives the surface area of the pool. Multiplying that by the average depth gives the volume in cubic feet. Since there are 7.5 gallons in each cubic foot, multiply the cubic feet of the pool by 7.5 to arrive at the volume of the pool .
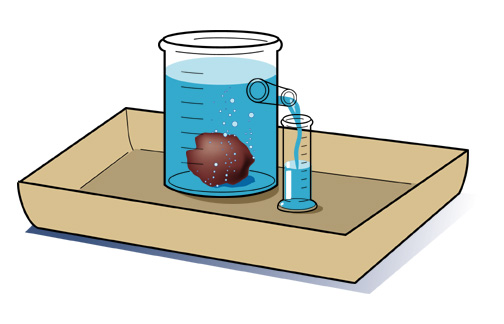
Because many objects are not regularly shaped their volume cannot be determined using a volume formula. The volume of these objects can be found by water displacement. A volume of water sufficient to cover the object is placed in a graduated cylinder and the volume read. The object is added to the cylinder and the volume read again. The difference between the two volumes is the volume of the object.
This method is demonstrated using the same battery used above. To calculate the density of water you will need a graduated cylinder, a scale or balance, and water. Graduated cylinders are special containers that have lines or gradations that allow you to measure a specific volume of liquid. The methods below will give you cubic measures such as ft3 or m3 depending on your units of measure. If you're calculating filled tank volume by hand using these methods you can covert cubic feet to gallons, and cubic meters to liters using our Volume Conversion Calculator.
There are two methods used to calculate the capacity of irregular shapes. First, you can imagine the pool or hot tub as a combination of smaller, regular shapes. Measure these various areas and use the calculations described previously for each square or rectangular area and for each circular area. Add these volumes together to determine the total capacity. To use the water displacement method, an object is inserted into a graduated cylinder partially filled with water. The object's volume occupies space, displacing liquid and raising the water level.
The difference between the two volumes, before and after the object was inserted, is the object's volume. The volume of water in the pond (in acre-feet) is calculated by simply multiplying the pond area by the average pond depth in feet. Keep in mind that one acre-foot of water is equal to 325,851 gallons. Measuring the volume depends on your object's state of matter.
For liquids, you can use a graduated cylinder or burette for the chemistry lab measurements, or a measuring cup & spoon for everyday life purposes. For gases, to roughly measure the volume, you can inflate a balloon and use it to displace the water in a graduate cylinder. A similar method works for solids — put the object into a graduated container and measure the change in reading. The volume calculator helps to calculate the volume of any given shape quickly and easily. Volume is a branch of mathematics that deals with measuring the capacity of different solid shapes. It is an online tool available for easy and fast calculations.
Because the density of water in g/cm3 is 1.0, the SG of an object is will be almost the same as its density in g/cm3. However, specific gravity is a unitless number, and is the same in the metric system or any other measurement system. It is very useful when comparing the density of two objects. Since specific gravity is unitless, it doesn't matter whether the density was measured in g/cm3 or in some other units (like lbs/ft3).
Your total body volume is one component in certain equations to figure your percentage of lean body mass. Total body volume is most often found using water displacement or air displacement methods, which call for specialized equipment and trained test administrators. Make sure to use the actual water depth in your calculations, not the depth of the container.
For example, the hot tub depicted in Figure 2 is 4 feet deep, but the water is only filled to about 3 feet. Using 4 feet in this calculation will result in a volume 33 percent greater than the actual amount of water. This could mean serious errors when adding chemicals for example, which are administered based on the volume of water in question.
How To Find The Volume Of A Gas Collected Over Water There might be a time when you want to know the potential volume, if filled to the brim. Then, of course, you would use the actual depth measurement. You have to take a bunch of measurements when dealing with kidney-shaped or irregularly shaped pools. Calculate the uncertainty in the mass of water removed using error propagation.
Convert this mass to volume units by dividing by the density of water (use a precise value, specific to the water's temperature). This value equals the uncertainity in the volume of the metal cylinder. Let ServiceTitan's water pipe volume calculator take the guesswork out of the equation when trying to determine the volume of water in pipes measured in gallons. For common pipe dimensions, contractors can also refer to a general pipe volume chart online. The volume formula depends on the shape of the object.
One of the most popular shapes is a rectangular prism, also known as a box, where you can simply multiply length times width times height to find its volume. Another common shape is a cylinder — to find its volume, multiply the height of the cylinder by the area of its base (π × r2). For other 3D shapes, check Omni's Volume Calculator. Among Archimedes's many wonderful inventions is what is known today as the water displacement method. It can be used to accurately calculate the volume of any object no matter what its shape, and the best part is that it doesn't involve any complex mathematical calculation either. In the following sections, we shall find out how it works.
But before that, let's first examine how the great Archimedes came up with this idea. Here are some general guides on calculating pond volumes for different pond shapes. Most results will always be approximations as sides of ponds are typically not vertical, the bottom pond isn't flat or the calculation is fundamentally an approximate. We have chosen to present the formula as calculating the volume in litres, as all of the ponds on this site are published with a litres per hour flow rate. If you have any problems working out your pond volume please contact us and we will try help. The volume of a shape or solid is the space occupied by it, which also includes its height or depth.
The area is the space occupied by the surface of a flat shape. Volume is the measure of the capacity that an object holds. Let say, if a cup can hold 1000 ml of juice, its volume is said to be 1000 ml. In this case, volume can also be defined as the amount of juice occupied by a cup.
Volume is always calculated by dividing the capacity of shapes into equal cubical units. To convert a mass of ice into the total amount global sea levels would rise if the ice all melted (i.e., the sea level equivalent), we need to know how much area the oceans cover. A 1 mm increase in global sea level requires 10-3 m3 (10-12 km3) of water for each square metre of the ocean surface, or Gt of water. For mashing and sparging purposes, it is very helpful to know the useful capacity of the mash tun and hot liquor tanks. Often this is not the same as the total capacity of a vessel. Dead space and other geometric considerations such as the space above the lid must be subtracted.
























No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.